Schizophrenia : People with this illness have changes in behavior and other symptoms — such as delusions and hallucinations — that last longer than 6 months. It usually affects them at work or school, as well as their relationships.
Schizoaffective disorder: People have symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder, such as depression or bipolar disorder.
Schizophreniform disorder: This includes symptoms of schizophrenia, but the symptoms last for a shorter time: between 1 and 6 months.
Brief psychotic disorder: People with this illness have a sudden, short period of psychotic behavior, often in response to a very stressful event, such as a death in the family. Recovery is often quick — usually less than a month.
Delusional disorder : The key symptom is having a delusion (a false, fixed belief) involving real-life situations that could be true but aren’t, such as being followed, being plotted against, or having a disease. These delusions last for at least 1 month.
Shared psychotic disorder (also called folie à deux): This illness happens when one person in a relationship has a delusion and the other person in the relationship adopts it, too.
Substance-induced psychotic disorder: This condition is caused by the use of or withdrawal from drugs, such as hallucinogens and crack cocaine, that cause hallucinations, delusions, or confused speech.
Psychotic disorder due to another medical condition: Hallucinations, delusions, or other symptoms may happen because of another illness that affects brain function, such as a head injury or brain tumor.
Paraphrenia: This condition has symptoms similar to schizophrenia. It starts late in life, when people are elderly.
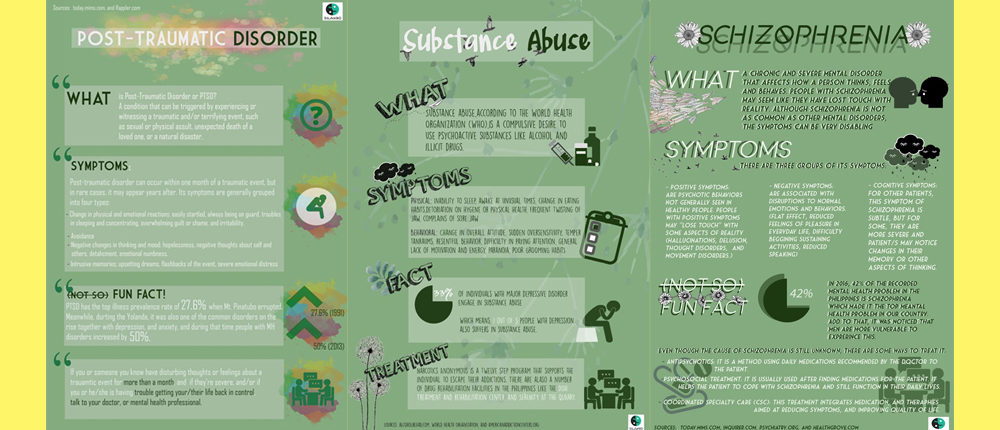
Thea Panganiban compiles and condenses basic information about post-traumatic stress disorder, substance abuse disorder and schizophrenia into these infographics